Properties of water
Properties of water
Properties of water
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
water, oxidane
| |||
| Other names
Hydrogen oxide, Dihydrogen monoxide(DHMO), Hydrogen monoxide, Dihydrogen oxide, Hydrogen hydroxide (HH or HOH), Hydric acid, Hydrohydroxic acid, Hydroxic acid, Hydrol,[1] μ-Oxido dihydrogen
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
| |||
| 3587155 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| 117 | |||
PubChem CID
| |||
| RTECS number | ZC0110000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| Properties | |||
| H 2O | |||
| Molar mass | 18.01528(33) g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid or almost colorless, transparent, with a slight hint of blue, crystalline solid or liquid[2] | ||
| Odor | None | ||
| Density | Liquid:[3] 0.9998396 g/mL at 0 °C 0.9970474 g/mL at 25 °C 0.961893 g/mL at 95 °C Solid:[citation needed] 917 kg/m3 = 0.917 tonne/m3= 0.917 kg/l = 0.917 g/cm3 ≈ 57.2 lb/ft3 | ||
| Melting point | 0.00 °C (32.00 °F; 273.15 K)[a] | ||
| Boiling point | 99.98 °C; 211.96 °F; 373.13 K [4][a] | ||
| Solubility | Poorly soluble inhaloalkanes, aliphatic andaromatic hydrocarbons,ethers.[5] Improved solubility in carboxylates, alcohols,ketones, amines. Miscible with methanol, ethanol,propanol, isopropanol,acetone, glycerol, 1,4-dioxane, tetrahydrofuran,sulfolane, acetaldehyde,dimethylformamide,dimethoxyethane, dimethyl sulfoxide, glycerol,acetonitrile. | ||
| Vapor pressure | 3.1690 kilopascals or 0.031276 atm[6] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.995[7][b] | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 13.995 | ||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.6065 W/m·K[9] | ||
Refractive index(nD)
| 1.3330 (20°C)[10] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.890 cP[11] | ||
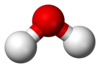
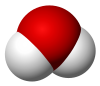
| Structure | |||
| Hexagonal | |||
| C2v | |||
| Bent | |||
| 1.8546 D[12] | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 75.375 ± 0.05 J/mol·K[13] | |||
Std molar
entropy (S | 69.95 ± 0.03 J/mol·K[13] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH | -285.83 ± 0.040 kJ/mol[5][13] | ||
Gibbs free energy(ΔfG˚)
| -237.24 kJ/mol[5] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Drowning Water intoxication Avalanche (as snow) (see also Dihydrogen monoxide hoax) | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations
| Hydrogen sulfide Hydrogen selenide Hydrogen telluride Hydrogen polonide Hydrogen peroxide | ||
Related solvents
| Acetone Methanol | ||
Related compounds
| Water vapor Ice Heavy water | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
| Infobox references | |||
Water (H
2O) is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, nearly colorless with a hint of blue. This simplest hydrogen chalcogenide is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" for its ability to dissolve many substances.[14][15] This allows it to be the "solvent of life".[16] It is the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas in nature.[17]
2O) is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, nearly colorless with a hint of blue. This simplest hydrogen chalcogenide is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" for its ability to dissolve many substances.[14][15] This allows it to be the "solvent of life".[16] It is the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas in nature.[17]
Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to separate ions in salts and strongly bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity.
Water is amphoteric, meaning it is both an acid and a base—it produces H+ and OH− ions by self ionization. This regulates the concentrations of H+ and OH− ions in water.
Due to water being a very good solvent, it is rarely pure and some of the properties of impure water can vary from those of the pure substance. However, there are also many compounds that are essentially, if not completely, insoluble in water, such as fats, oils and other non-polar substances.